LDL cholesterol and lipoprotein (a) cholesterol are more likely to stick to your arteries and lead to dangerous heart events
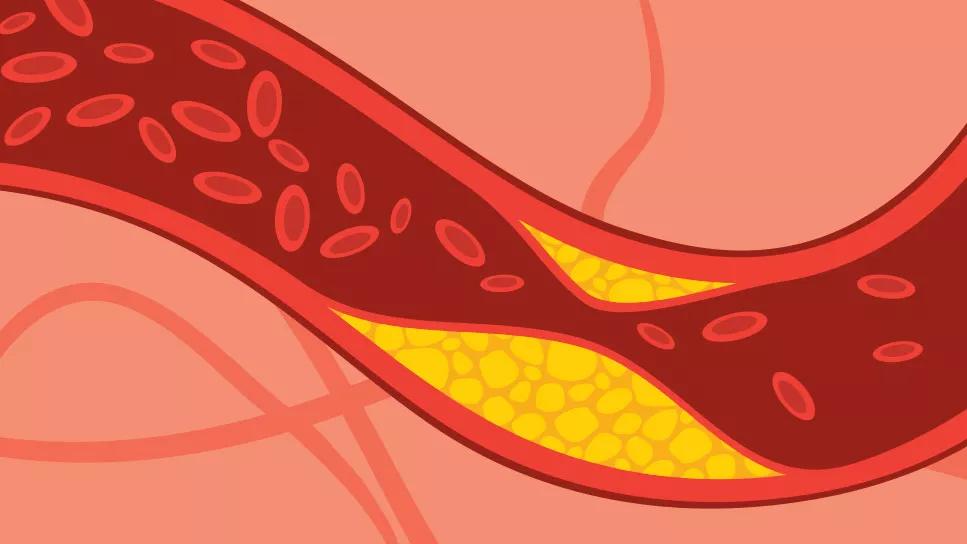
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/82d8fc23-5fe6-4f5f-937d-6140a76f6f9d/cholesterol-artery-619740204)
Cholesterol blocking blood flow in artery
You’ve probably heard about the dangers of high cholesterol. But what you may not know is that cholesterol isn’t just one thing. “Cholesterol” is actually an umbrella term for a few different lipids (fats) in your blood.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
And some of those lipids are more dangerous than others.
“The type of cholesterol that we get concerned about are the cholesterol molecules that can ‘stick’ to the inside of the arteries and cause plaque formation,” clarifies cardiologist Ashish Sarraju, MD.
What kinds of cholesterol are sticky? And what can you do about it? Dr. Sarraju shares what you need to know about sticky cholesterol.
Sticky cholesterol isn’t an actual medical term. But it’s a fitting way to help explain the way that some types of cholesterol pose a risk to your well-being.
“When people talk about sticky cholesterol, they’re really talking about the LDL cholesterol particles that contribute to plaque buildup and adverse heart outcomes,” Dr. Sarraju explains.
Let’s break that down a bit.
In healthy ranges, cholesterol does an important job of keeping your body healthy by carrying fats through your bloodstream. But too much of certain kinds of cholesterol gums up the works.
There are two main kinds of cholesterol:
Advertisement
And there’s one type of particle that’s similar to LDL cholesterol that’s notoriously sticky. It’s called lipoprotein (a), or Lp (a) for short.
“The subset of cholesterol particles that we really want to try to control and reduce are the ones that cause plaque and blockages,” Dr. Sarraju emphasizes. “Reducing those can reduce the risk of heart attacks, strokes and death. LDL cholesterol and Lp (a) are the sticky cholesterol we want to keep in a healthy range.”
As your blood travels through your arteries, it carries HDL, LDL and Lp (a) cholesterol molecules through your body.
HDL cholesterol travels along without a problem. But if you have high levels of LDL cholesterol or Lp (a) molecules, they may as well be coated in super glue.
As they bump up against your artery walls, they grab hold and don’t let go, hanging around inside your artery walls. That’s called arterial plaque.
More blood, carrying more LDL cholesterol and Lp (a) molecules, comes by. They also glue themselves to your artery walls and the plaques. Over the years, those plaques become bigger and bigger as more sticky cholesterol is deposited. That can lead to atherosclerosis, a condition where your arteries become harder and narrower due to plaque formation.
As time goes by, it gets harder for blood to get through the narrowed arteries. And it takes a big toll on your body.
“Plaque buildup can cause a host of adverse outcomes,” Dr. Sarraju warns.
For example:
Dr. Sarraju reminds us that high cholesterol often doesn’t cause symptoms.
“High cholesterol and high blood pressure — these are silent killers,” he cautions. “You only know if you’re at risk for plaque formation if you get your lipid levels checked. Or if, unfortunately, it’s found after a major medical event, like a heart attack.”
Keeping up with regular screenings with a healthcare provider is the best way to keep tabs on your cholesterol.
Lipid screenings are a pretty routine part of a regular physical exam. And while those blood tests can share insight into your HDL and LDL cholesterol numbers, they don’t typically test for Lp (a). If you or your provider are concerned about your risk for Lp (a), further blood tests will be needed.
Advertisement
Even slightly elevated cholesterol levels should be addressed, Dr. Sarraju encourages. “Research has shown us that exposure to cholesterol is cumulative. The longer you’re exposed to heightened cholesterol levels, the more you’re at risk for plaque formation. And plaques typically don’t go away once they form.”
Your cholesterol levels are a matter of both your genetics and your lifestyle.
“There is a genetic component to how much cholesterol your body makes,” Dr. Sarraju says. “Lp (a) is especially known to be inherited.”
A genetic component, yes. But your family history isn’t a destiny.
Choices you make can also help keep your cholesterol at a healthy level. That includes things like:
But even with these steps, your healthcare provider may prescribe medications to keep your cholesterol at a healthy level.
“We want people to do their best with a healthy lifestyle as a fundamental step because it will help your body stay healthy in so many ways,” Dr. Sarraju affirms.
Advertisement
“If LDL cholesterol doesn't significantly change with lifestyle changes, taking medication isn’t a personal failing. It’s just that in your case, we need to take additional steps, possibly because of genetics. But maintaining healthy habits is important — no matter your genetics and no matter if you’re taking medication.”
Sticky cholesterol isn’t always something you can manage on your own. But with a healthy lifestyle and close cooperation with your healthcare provider, you don’t have to get stuck with high cholesterol.
Advertisement

Delivered every Tuesday!
Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more
It's a letter about the news!

Every two weeks once
Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about our editorial process.
Advertisement
If you’re eating more than one egg per day, you might want to cut back
Your family tree may increase your risk of high cholesterol and heart disease
Understanding the difference between ‘lousy’ and ‘healthy’ cholesterol can help you keep your heart healthy
Spoiler alert: The potential benefits of drinking alcohol may be a tad overstated
An expert explains the link
The right lifestyle changes can make all the difference
Not all cholesterol-rich foods are bad for you
The short answer from a cardiologist
Type 2 diabetes isn’t inevitable with these dietary changes
Applying a hot or cold compress can help with pain
Pump up your iron intake with foods like tuna, tofu and turkey