From heritage to hormones, there are many reasons why you might sprout a little chin hair
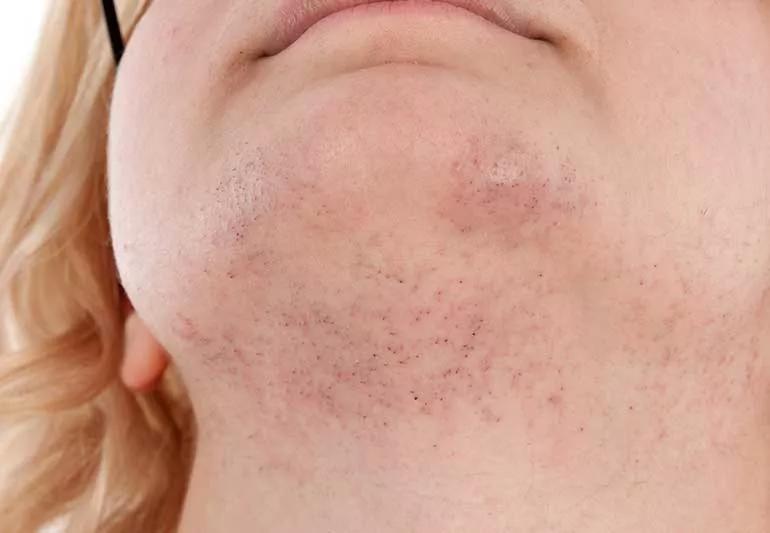
It’s a common experience: Discovering a hair — or several — where you aren’t expecting it. Sometimes, the discovery is a cause for celebration or laughter. Other times, you may find yourself greeting the new hair with dismay, straight-up confusion … or a pair of tweezers.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Some women and feminine-presenting people find the presence of hair on their chin or jawline particularly upsetting. Despite being a normal result of the many hormonal changes we experience over the course of our lives, many cultures associate facial hair with masculinity.
What some view as a simple stray whisker can be devastating to others’ self-identities and self-concepts — and occupy big chunks of their daily lives. A 2006 study found that women living with unwanted facial hair reported high levels of anxiety and depression and spent, on average, 104 minutes on facial hair removal and maintenance every week.
To further complicate a discussion of facial hair in women and people assigned female at birth (AFAB), facial hair is not a uniform characteristic. Some people are naturally hairier than others. That means one person’s “normal” hair growth and pattern may be a symptom of a health issue in another.
It’s a lot to wrap your head around. That’s why we talked to endocrinologist Vinni Makin, MD, about the many causes of hair on your chinny chin chin — and different options for removing unwanted facial fuzz.
In order to tackle this hairy subject, a few definitions are in order:
Advertisement
Hormone changes like those we all experience during puberty can turn vellus hair into terminal hair. When we go through puberty, we’re producing more hormones — specifically, our body begins producing more androgens (also known as sex hormones or “male hormones”).
Regardless of our biological sex, we all see some of our vellus hair turn into terminal hair in what are called androgen-dependent areas of the body — places like your underarms and around your genitals. As androgen levels go up, so, too, does the amount of face and body hair you develop. You also become capable of growing hair in more places, including your knuckles, back, stomach, buttocks and chest — areas typically associated with men and people assigned male at birth (AMAB).
When your hormone levels fluctuate, the amount and type of hair on your body can change. For women and people AFAB, those hormone fluctuations occur throughout your life, including during puberty, pregnancy and menopause. This is totally not only normal, but it’s a good thing.
So, you may find a new hair or two on your chin that you never had before. You may also find that the amount of new hair you have goes well beyond one or two new strands. If you’re experiencing new, thick, coarse hair anywhere on your face or body, this typically falls into one of two categories:
Whether it’s a few new hairs or decidedly more than just a few, there are several different reasons this could be happening. We’ve collated some of the most common causes of facial hair in women and people AFAB below:
For women and people AFAB, hair growth on the chin and jawline can be a part of getting older. The hormonal changes that come with menopause impact both your head and body hair. While it may be unpleasant, it’s not unusual to feel the texture of your head hair change — and even notice hair loss — at the same time your upper lip and jawline start to get fuzzy. If these changes are happening very quickly, they might be cause for concern and medical evaluation.
Advertisement
A large proportion of the people who come to Dr. Makin with complaints about chin hair do so as part of a larger — and seemingly opposite — concern caused by a hormone imbalance: scalp hair loss. That’s because when your body is producing too many androgens like testosterone, it will cause hair loss on your head and growth on your face.
Polycystic ovary syndrome is one of the conditions that may run in families. What we know for sure is that it’s a very common endocrine condition: Somewhere between 5% and 15% of women of reproductive age have the condition, which causes a wide range of complications from irregular periods and acne to a significantly elevated risk of Type 2 diabetes.
PCOS disrupts your endocrine system, causing an overproduction of androgens. That hormone imbalance can cause hair growth in androgen-dependent areas of the body and scalp hair loss. It’s one of the most common causes of hirsutism, with severe cases sometimes causing women and people AFAB to develop full beards.
Sometimes, the reason you’ve got a bit more hair on your face than other people comes down to your family tree. For some people, they’re inheriting physiological traits associated with a geographic location or ethnic group. For example, hirsutism is most common in people of Southeast Asian, Mediterranean and Middle Eastern descent — and less common, Dr. Makin says, in Native American and East Asian women.
Advertisement
While we don’t know exactly why, there’s a clear correlation between insulin resistance and hyperandrogenism, even in people who don’t have PCOS. It’s not unusual, then, for women and people AFAB living with diabetes to notice an increase in body and facial hair at the same time that the hair on their head is thinning.
Excessive hair growth — on both your face and other areas of your body — is a common symptom of a rare condition called Cushing syndrome. People with Cushing have too much cortisol in their body, either because their body produces too much of the hormone or as a side effect of a medication.
“Congenital adrenal hyperplasia” is an umbrella term that describes a range of different adrenal gland disorders. Some people are born with these conditions, while others experience them later in life.
When we lose or gain a significant amount of weight in a short period of time, it messes with our hormones. The resulting imbalance often results in an increase in facial hair. In fact, some people with eating disorders like anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa develop lanugo, the fine hair that covers fetuses in the uterus.
There are a number of medications that count hair growth as a side effect, including anabolic steroids, as well as certain kinds of chemotherapy and epilepsy treatments.
Advertisement
Separately, some transwomen and feminine-presenting people may find that even when taking hormone therapy as part of the gender affirmation or transition process, some facial hair growth will continue.
Chin or facial hair on women and people AFAB is not, in and of itself, a medical concern. What is a medical concern, Dr. Makin explains, are the feelings that extra hair sometimes brings with it.
“Every person has a different level of comfort with it,” she continues. “For some people, a few stray hairs can be emotionally distressing, while others might have much more hair growth and don’t feel bothered by it. It’s the individual’s level of comfort that’s important.”
There are other factors to consider as well.
“Some interventions are really expensive, but there are cheaper options, too. What we choose also depends on the degree of hirsutism and the person’s pain tolerance,” Dr. Makin adds.
Here are some options for removing unwanted facial hair:
If you’re concerned about your facial hair, it’s a good idea to talk to a doctor about it. While a primary care physician is a good place to start, Dr. Makin suggests requesting a referral to an endocrinologist.
“I always worry that primary care physicians are already addressing a lot of health issues for every patient in a short appointment,” she explains. “A visit to an endocrinologist would be a good idea because they can focus exclusively on this complaint, investigate it appropriately and tell you if there’s a cause that we can cure or control.
When you meet with an endocrinologist about facial hair, Dr. Makin says there are basic questions you’re likely to get.
The first question is, “Has there been a recent worsening of the hair growth?” Dr. Makin asks this question because — in addition to PCOS and adrenal enzyme issues — tumors in your adrenal glands and ovaries can cause a rapid worsening of hair growth and irregular periods in people who menstruate.
In addition to worsening hair growth and irregular periods, your endocrinologist will probably ask if you’re experiencing any of these symptoms:
Your answers to these questions will determine the doctor’s next steps. Dr. Makin explains her process: “If there are no other symptoms, then, chances are you have idiopathic hirsutism, which could be racially or ethnically associated. I’ll always test my patients’ hormones to make sure I’m not missing anything, but if the hormone levels are within a healthy range, the priority becomes controlling unwanted facial hair.”
For better or worse, many societies teach us to see our hair as an expression of who we are. That can make any change — whether it’s a bad haircut, going gray or balding — emotionally difficult, regardless of your gender identity or expression.
Whether you’re sporting peach fuzz or a full beard, remember: You have a right to be fond of your face. That may mean removing your facial hair or seeking medical intervention … and it may not! Do whatever makes you happy and keeps you healthy — both physically and mentally.
Learn more about our editorial process.
Advertisement

Try limiting heat styling and eating a healthy diet instead

Most recommended precautions center around minimizing bruising or swelling

Even one drink can have an impact on your cognitive function leading to slurred speech, blurred vision and impaired memory
Understand who may (and may not) benefit

Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet. Et odio Quis vel ipsam omnis eum alias deleniti et placeat impedit non voluptas galisum hic autem enim et cupiditate aliquid. Est beatae quidem non facilis autem ut commodi nisi aut tempore rerum et dolores voluptatem cum enim optio id sapiente quasi. Ad laboriosam officiis 33 cupiditate sequi ea voluptatum consectetur qui necessitatibus voluptate et quasi doloremque et facere explicabo quo explicabo officia

Seeking help through therapy can be an important step in improving your quality of life when you have UC

Type 2 diabetes isn’t inevitable with these dietary changes

Applying a hot or cold compress can help with pain