Many overlook the signs of a slow heart rhythm
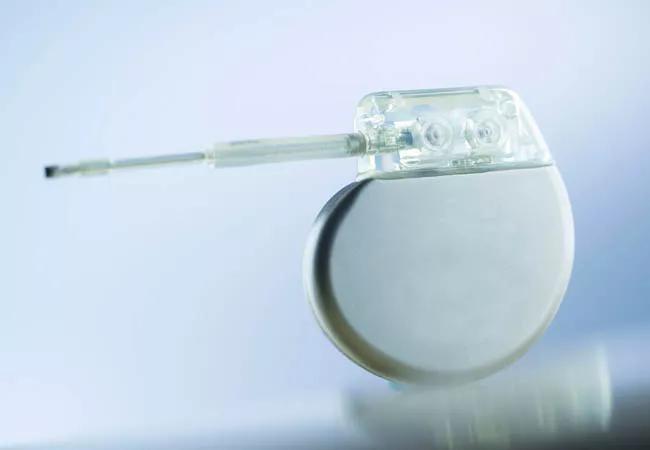
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/8352acf3-61c8-4bd0-9e60-bc7fdf115287/pacemaker09_jpg)
Small white pacemaker on white and blue background
When your heart beats too slowly, it needs help. Pacemakers — tiny implantable computers that speed up a slow heart rhythm — are the answer for millions of people, from newborns to 90-year-olds.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
However, “many people have no idea that they may need a pacemaker,” says cardiologist Bruce Wilkoff, MD. “Fainting — the clearest symptom of a slow heart rhythm, or bradycardia — is often their first clue.”
A slow heart rhythm deprives your organs of oxygen and nutrients. You can get lightheaded or dizzy when you stand up or exert yourself. You become short of breath and easily fatigued. You can pass out.
“Or you simply don’t feel good because your body isn’t getting enough blood to supply your need to breathe, move and think,” says Dr. Wilkoff.
Your upper heart’s right filling chamber (atrium) has a sinus node that controls, or paces, using electrical impulses that keep the heart beating in sinus rhythm.
It quickly adjusts your heart rate, which indirectly adjusts blood pressure as your metabolic needs change (for example, during rest or exercise).
When the sinus node doesn’t function, because of sick sinus syndrome or scars in your atrial heart muscle, your heart slows down — sometimes stopping for several seconds.
Heart block can also slow the heart. Here, the sinus node works fine. But the atrioventricular (AV) node doesn’t transmit its signals down from the atrium to the lower heart’s pumping chambers (ventricles).
Advertisement
“Heart block is like a cut wire in the heart’s electrical system,” explains Dr. Wilkoff. “The ventricles don’t get the signal they need, so they come up with a heartbeat on their own, which isn’t as good.”
Pacemakers are most often implanted in older patients who have acquired heart block or sinus node dysfunction.
“We implant pacemakers for patients in their 20s, 30s, 40s and 50s, but the average patient is 60-plus,” says Dr. Wilkoff.
When heart block is congenital, a pacemaker can be implanted right after birth, or in young adulthood when symptoms develop.
Pacemakers are usually inserted beneath the skin of your upper chest near the shoulder. Wires, called leads, run from the device into the heart using veins as the natural pathway.
Pacemakers are quite reliable. With each passing decade, they’re getting smaller and lasting longer.
“Today’s pacemakers are about the size of a big tablespoon, and the batteries last seven to 10 years,” says Dr. Wilkoff.
Little antennas in the devices allow doctors to collect information about each patient’s heart rhythm and pacemaker function. This allows them to customize pacemaker activity to fit the patient’s needs.
Pacemakers are monitored remotely while the patient is home, usually during sleep. “Most patients are amazed by their flexibility and sophistication,” says Dr. Wilkoff.
The newest pacemakers are leadless and work wirelessly. “They’re the size of a large jelly bean and sit in the ventricle. But they’re not suitable for every patient,” he notes.
With pacemakers, you can count on two things, he says: If you have bradycardia, they’ll help you feel and function a whole lot better. And the technology will continue to progress and evolve.
Advertisement

Delivered every Tuesday!
Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more
It's a letter about the news!

Every two weeks once
Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about our editorial process.
Advertisement
Complications related to the implanted device leads may go unnoticed
Pacemakers steady heartbeat, ICDs reset the heart
Your veins might look blue, but that’s not the color of the blood flowing inside
A psychologist shares ways to cope with a lack of closure
A Q&A on the controversial opioid withdrawal aid
How to see past outdated, prevailing attitudes and views
Studies highlight importance of social support
Type 2 diabetes isn’t inevitable with these dietary changes
Applying a hot or cold compress can help with pain
Pump up your iron intake with foods like tuna, tofu and turkey